|
Hemostasis is defined as the stoppage of bleeding or hemorrhage;
or the stoppage of blood flow through a blood vessel or body part.
In fact, hemostasis is a complex control system through which blood
is kept from leaking outside blood vessels. One of its main components
is a complex coagulation cascade involving numerous blood clotting
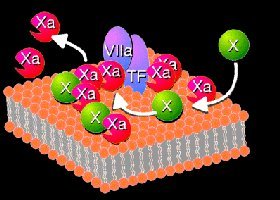
proteins or factors, platelets and tissue factor. Tissue factor
is a lipoprotein that is constitutively present on the membrane
of certain cells. When it is exposed, it binds to Factor VII (one
of the central coagulation factors) and activates the tissue factor
dependent coagulation pathway. Factor VIIa plays a pivotal role
in hemostasis.
|
|
|
Clinical
applications of hemostatic agents are rapidly growing in clinical
medicine. Because of the pivotal role of hemostasis in surgery,
critical care, trauma, perioperative medicine, and hematology, therapeutic
approaches to treating bleeding and bleeding problems are important.
Further, a broad spectrum of thrombin and platelet inhibitors have
assumed a pivotal role in clinical medicine, and many of these agents
are not readily reversible. Novel therapeutic approaches are important
to consider when managing patients with potential for severe life
threatening bleeding. This site will explore important issues in
managing these patients and understanding the clinical problems
they pose.
This site is sponsored by DocMD.com,
an Internet site dedicated to bringing useful information to physicians
and other healthcare personnel. Be sure to visit DocMD.com
to keep up on what is new and interesting in healthcare, and for
other helpful information. Please contact us at Info@DocMD.com
if you have additional suggestions or comments.
|



